Explosive welding
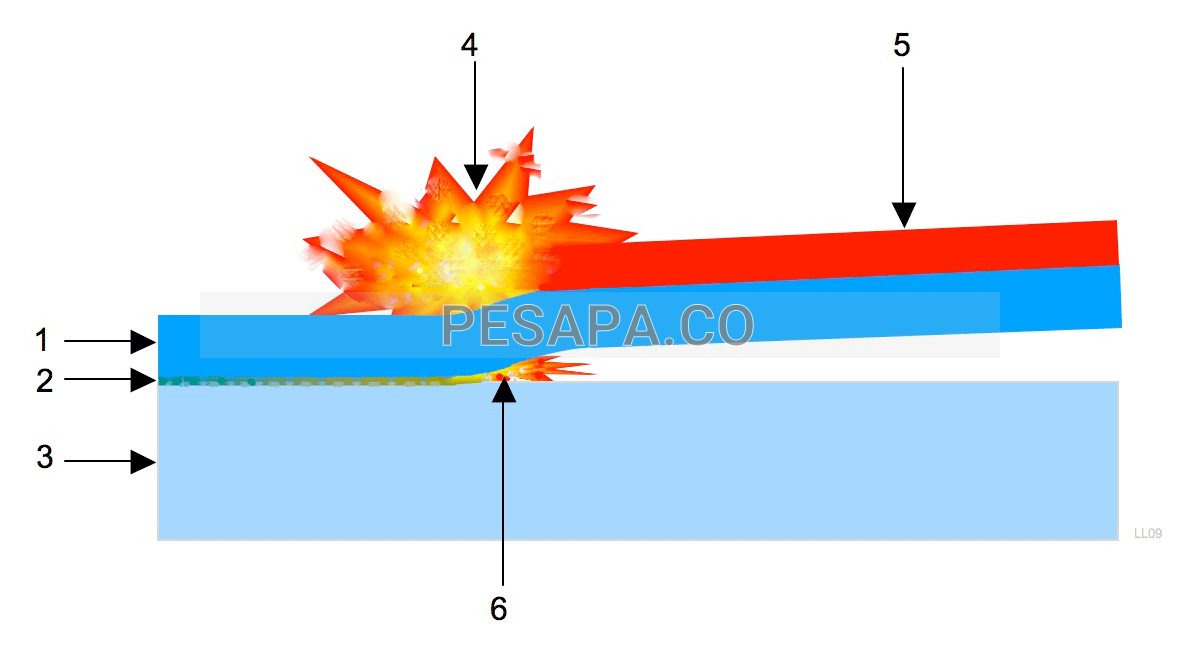
This type of welding is a solid-state welding process that is performed as a result of the collision of one of the components at a very high speed due to the use of explosives.
The most common use of this process is typically for coating or cladding carbon steel with a thin layer of corrosion-resistant material (such as stainless steel, nickel alloy, titanium or zirconium). Due to the nature of the process, the shape of the parts is very important and they should be simple in general. Commonly produced shapes are sheets, tubes and tube sheets.
Unlike other welding methods such as arc welding, which developed in the late 19th century, blast welding is a relatively new method and was developed in the decades after World War II. Of course, it dates back to World War I, when bullet debris was seen sticking to the armor plates of weapons (when in fact they were welded to the metal). Since heat played no role in this case, it was concluded that this phenomenon was due to the force of the explosion on the shattered particles or fragments. These results were later repeated in the laboratory and after sometime this process was recorded and used.
In 1962, Dupont patented the blast welding method, which was approved in January 1964 under U.S. Patent No. 3,137,937, identified by the Detailed trademark. In July 1996, Dynamic Materials Corporation acquired ownership of Detailed Processes for $ 5321,850. In Iran, Vetra Engineering Group has been working on explosive welding and other solid-state welding processes for nearly 10 years and has been able to provide valuable services in this field, one of the highlights of this series of welding simulations before Explosive operations and accurate calculation of the composition and number of explosives.
Benefits of Explosive Welding:
1-Explosive welding can be used to connect and weld most metals and alloys that cannot be welded by conventional welding methods (Vetra Company has welded most of the alloys used in the country’s industry in various projects in this way).)
2-Explosive welding method does not melt the metals, instead it introduces the surfaces of both metals into the plasticization area, which causes sufficient initial contact to create welding. As a result, no melting defects will occur in the alloys (such as welding aluminum and copper). The principles of this method are similar to other non-melting welding methods such as friction welding.
3-Large surfaces in explosive welding can be connected to each other very quickly and the weld itself is very clean because the surface wastes in both metals are removed from the contact area with great intensity during the reaction.
One of the most important advantages of blast welding is their application in the bonding of heterogeneous metals. Coating large plates to make composite plates for use in the construction of pressure vessels, creating cylindrical joints such as pipe-to-pipe welding and tubing in a defective heat exchanger, pipe-to-pipe connection in all directions and double-walled, thin-sheet edge welding and the manufacture of reinforced wire composites are among other applications of blast welding. The mechanical and metallurgical properties of explosive welds are important. Determining the strength and quality of the bond between a thin coating layer and a thicker plate is difficult for any method, and explosive welding is no exception. In general, the metallurgical problems of this type of welding are not as severe as fusion welding.

